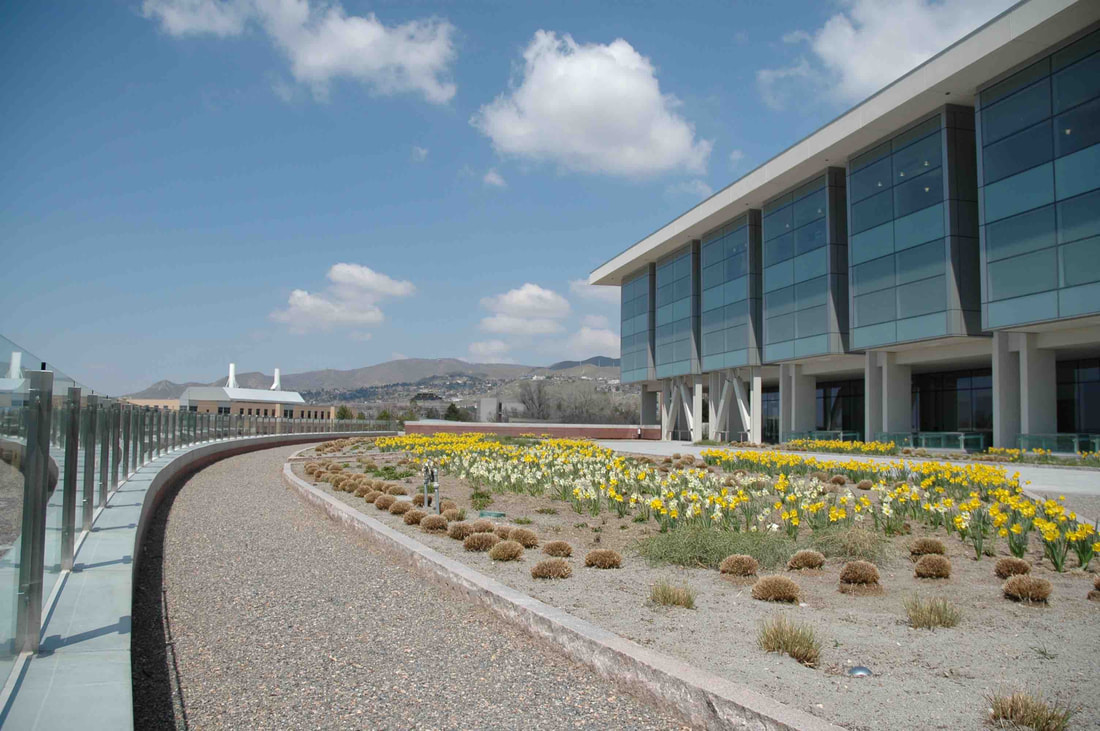
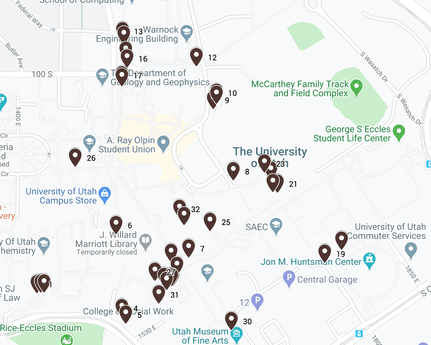
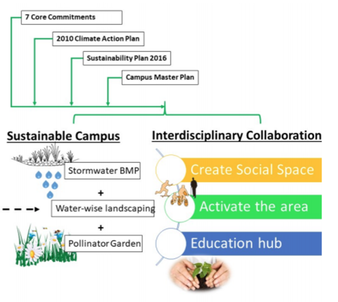
Green infrastructure describes plant assemblages constructed to provide an ecological service
On our campus, you will find many different designs of green infrastructure, some of which we will see on our campus walk. While collections of plants often serve valuable aesthetic functions, green infrastructure is a term that describes plant assemblages constructed for a specific ecological service or function. Some are designed to capture stormwater and street pollutants. Others function as hot spots for native pollinators. Still others serve to cool the tops of buildings. The Center for Ecological Planning + Design is developing a Landscape Lab in Research Park to explore the benefits and functionality of different green infrastructure designs and different species compositions that may provide a variety of ecological services. By the end of this walk, students will be able to (a) distinguish three different kinds of green infrastructure on campus, (b) identify key species associated with stormwater management systems, and (c) recognize stormwater flow connections that relate to the size of the green infrastructure.
Click here for a handout to help guide you if you wish to take this walk on your own.
Click here to download questions to be answered about this campus walk.
Click here for a handout to help guide you if you wish to take this walk on your own.
Click here to download questions to be answered about this campus walk.
|
Stormwater run-off green infrastructure
|